Making A Difference With Carbon Insetting
Carbon Insetting - The Future for Carbon Projects
Introduction
Carbon insetting involves reducing carbon emissions within a company’s own supply chain rather than offsetting them through external projects. Initial research on carbon insetting has found it to be far more effective than offsetting schemes which have faced controversies around veracity & impact.
In the wine industry, carbon insetting might involve supporting vineyard owners in adopting regenerative agricultural practices, improving energy efficiency in production facilities, or enhancing the sustainability of packaging. Deep Planet is proud to be partnering with a number of organisations globally to help our customer base begin their insetting journey.
Why Carbon Insetting Matters
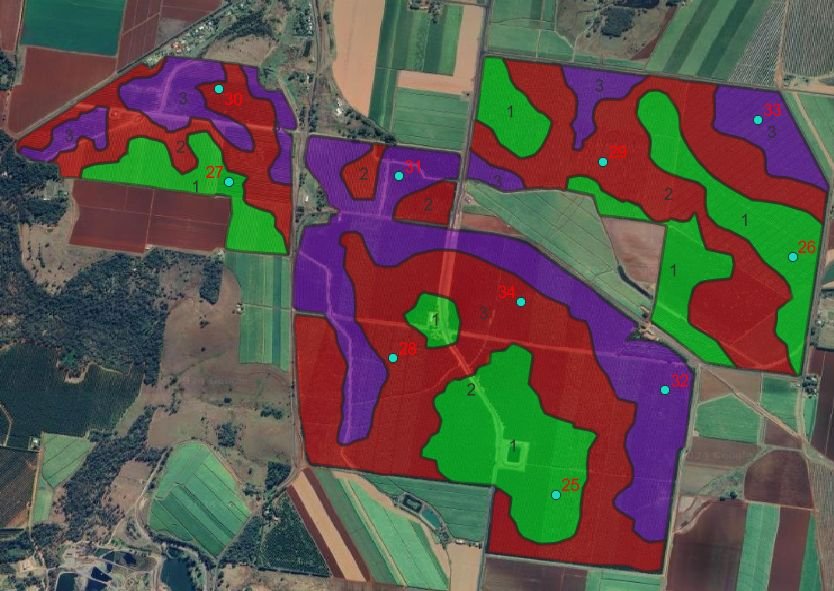
Automated zoning of vineyards and bespoke soil sampling plans help users to reduce costs associated with Monitoring, Reporting & Verification.
With increased pressure on businesses to reduce their Carbon Footprint, various standards have been developed for measuring and reporting carbon emissions. The Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol categorises emissions from businesses into 3 scopes:
Scope 1: Direct emissions from owned or controlled sources.
Scope 2: Indirect emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling consumed by the reporting company.
Scope 3: All other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain.
Scope 3 emissions typically represent the largest portion of a company’s carbon footprint and are notoriously difficult to measure and manage. For the wine industry, Scope 3 emissions include those generated by suppliers, transportation, and even the use and disposal of wine bottles by consumers.
Carbon insetting aligns closely with efforts to reduce Scope 3 emissions. Here’s how it can be particularly beneficial for retailers, importers and distributors in the wine industry:
More Effective Reduction of Carbon Footprint: By investing in regenerative viticulture within their supply chains, wine businesses can directly influence and reduce their carbon footprint through reduced emissions and increased carbon sequestration. This targeted approach is often more effective than external offsets.
Enhanced Supplier Relationships: Supporting suppliers in adopting regenerative practices can strengthen relationships and create a more resilient and sustainable supply chain. This collaboration can lead to mutual benefits, including cost savings, improved product quality and supply security.
Consumer Appeal: Modern consumers are increasingly environmentally conscious. Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability through tangible actions within the supply chain can enhance brand reputation and loyalty. One way to communicate sustainability and regenerative agriculture efforts to consumers is through product carbon neutral certification.
Regulatory Compliance and Competitive Advantage: As regulations around carbon emissions tighten, businesses that proactively reduce their Scope 3 emissions through carbon insetting will be better positioned to comply with future requirements and maintain a competitive edge. The increased carbon sequestration due to regenerative practices creates an opportunity to generate verified carbon credits within the supply chain to offset emissions and meet carbon reduction targets.
However, developing a Carbon Insetting project is not without its hurdles. Deep Planet is helping users break down the barriers to commencing their own successful Carbon Insetting project.
How Deep Planet Helps
Measurement and Verification: Accurately measuring Scope 3 emissions and the impact of insetting projects can be complex. It requires robust data collection and analysis capabilities. Deep Planet’s soil organic carbon (SOC) monitoring tool supports wine businesses in measuring the impact of regenerative viticulture practices, understanding historical changes and trends in SOC variability and identifying opportunities for claiming verified carbon credits.
Initial Investment: Transitioning to regenerative practices and other sustainable initiatives often requires significant upfront investment. This is why Deep Planet partners with retailers and other wine businesses to design carbon insetting and regenerative viticulture projects that incentivise both suppliers and retailers.
Stakeholder Engagement: Successful carbon insetting requires buy-in from all stakeholders, including suppliers, employees, and consumers. Ensuring alignment and collaboration can be challenging but is essential for success.
Knowledge and Expertise: Implementing regenerative agriculture and other sustainable practices requires specialised knowledge and expertise. Deep Planet is here to offer our specialist industry knowledge, experience and tools to support your regenerative viticulture initiatives.
World Leading Research & Collaboration
Deep Planet has been helping our users to adopt sustainable, profitable regenerative practices for several years. You can read more about our work here:
Conclusion
By leveraging AI and satellite imagery, Deep Planet has been able to help our customers launch bespoke Carbon Insetting projects, helping growers move towards a more sustainable, data-driven future for agriculture. Reach out using the link below to get started with your own project today.
Unlock the Future of Crop Monitoring with AI-Driven Insights!
Discover how Deep Planet’s Soil Organic Carbon Monitoring tools could help you to slash cuts & reduce your environmental footprint.
Stay ahead of industry trends, optimize your vineyard management, and embrace sustainable practices with real-time analytics.